Over the past years, SEO has been changing constantly. Google has taken it very seriously that the users get the right content for the queries they search for. And for that, numerous updates have been made in their algorithms from the past year.
These are the updates Google has made in its algorithms in the year 2013.
- Panda #24 – January 22, 2013
- Panda#25 – March 14, 2013
- Phantom – May 9, 2013
- Domain Crowding – May 21, 2013
- Penguin 2.0 – May 22, 2013
- PayDay Loan Update – June 11, 2013
- Panda Dance – June 11, 2103
- Multi-week Update – June 22, 2013
- Panda Recovery – July 18, 2013
- Knowledge Graph Expanision – July 19, 2013
- Humming Bird – August 20, 2013
- Penguin 2.1 – October 4, 2013
- Authorship Shake-Up – December 19, 2013
Now, let’s see what updates Google has made in the year 2014, till date.
- Page Layout #2 – February 6, 2014
- Unnamed update – March 24, 2014
- PayDay Loan 2.0 – March 16, 2014
- Panda 4.0 – May 19, 2014.
There is still half an year to go and experts are expecting a lot more updates to come from Google. Here’s the list of all Google’s SEO algorithms since 2000 and their updates. More on Google Panda and Google Penguin Updates. Check out all the Google algorithm updates in its history.
NOTE : if you are new to these technical terms like panda and penguin – then go through the following links
- What is Google Panda Update
- What is Google Penguin Update
- Difference between the Panda and Penguin Updates
Here are a few SEO Tips and Tricks for 2014 that will help you go.
1 # : I observed one interesting thing in this 2014 that – even if it a smaller or larger site – We Can Rank (this is for small websites owners  ) ! Previously this is not the situation and small websites owners never tried big fearing bigger sites about their authority in Google. And I have seen seen so many positive results which I cannot share and this will be a good factor.
) ! Previously this is not the situation and small websites owners never tried big fearing bigger sites about their authority in Google. And I have seen seen so many positive results which I cannot share and this will be a good factor.
 ) ! Previously this is not the situation and small websites owners never tried big fearing bigger sites about their authority in Google. And I have seen seen so many positive results which I cannot share and this will be a good factor.
) ! Previously this is not the situation and small websites owners never tried big fearing bigger sites about their authority in Google. And I have seen seen so many positive results which I cannot share and this will be a good factor.
2 # : Please don’t go after backlinks : Better concentrate creating more quality content and dont waste too much in getting backlinks (either money or time).
3 # : STOP DOING guest posts to obtain links. Google already made several announcements about this.
4 # : TRY to engage the viewers (with commenting and feedback) and also make sure that you make PERFECT navigation in the site to make sure that users/visitors can navigate through the content without any complexity.
5 # : Google Panda 4.0 Hit Sites Blocking CSS and JavaScript – this is a news from Seroundtable.com where they told that some people reported them – So try avoiding this in case if you are penalized in this recent Google Panda Update. Here is one live example how a person named Joost (developer) recovered his site from this similar issue. Check this link.
Here are some more essential things that one should follow to maintain the Rankings
#1 Have a Responsive Web Design
There has been a drastic growth in the use of smartphones and tablets, in the past few years. And most of those users prefer browsing the internet through those devices. Make sure that the content of your website is easily readable when viewed through all other devices like such; in short, improve your website’s responsive design. This is a very important factor that can affect your SEO since, if your website doesn’t provide a good user interface, the user will shift to something that does.
#2 Use Social Media
Publicizing your article on Social Media is a very important technique to, not only get more hits, but also to improve your SEO. Google Plus’s +1 carries around 0.37% of the weight-age of your page’s SEO. So, the better you reach out to people on Social media, the better it is for your website. Still there is lot of
#3 Brand building – Authorship
Although Google has recently announced that they will remove the authorship images from search results, SEO experts, after many experiments, say that authorship can still affect a website in a positive manner.
However, only the image is dropped off and authorship stays in the website. To set up authorship you will need a Google+ account. Still today, no one from the SEO industry could confirm the importance of the authorship verified content in search rankings either in the form of some SEO experiments or cases, even google never confirmed it – but still there is a big question about its factor.

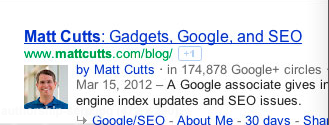
This is how authorship mark up will look in the search results.
#4 Go with a Content Management System (CMS)
Use a proper content management system that offers various plugins. WordPress is one of the most used content management systems, nowadays. It not only provides you with amazing plugins, but will also help you frame your content and images in a way which will make it easier for Google bots to traverse. Although, using a CMS is not a must, it is highly advisable. Blogspot and Drupal are a couple of other famous CMS.
#5 Have a killer UX
Good User Experience (UX) can lead you to great results. See that the navigation from one page to another inside the site, is easy, even for a normal user to do. Also, see that the loading time of the website is minimal, not only on a PC, but also on other devices. Learn more about UX and make the most out of it.
#6 Get a good Domain Name
Domain name? you may ask. Yes. See that the domain name is relevant to the content you are planning to produce in the site. Having the main base word/keyword of the website in your domain name can turn out to be very helpful. Choose a classy name and not a funny/silly name. Generally, such silly named websites are not taken seriously.
Finally I would say its just a factor and its not compulsory to make a domain name keyword related to your niche – because Branding is also an alternative for that. If you have one then its GOOD because I still see lot of niche sites ranking for the keywords and the search engine still recognizes it even after many panda and penguin updates.
#7 Keyword Analysis
Look for keywords that have low competition and high search volume. This will help you write articles using such words as the keywords and gain more users. Google Keyword Planner is a free SEO tool that will help you find such words. Instead of using a single word, it is advised to use key phrases. And also, make sure that you know how to use a keyword in the context. However, the most important of things is to produce good quality content that your readers would connect to.
#8 Link Building
See that you first build proper inter links among the pages of your website so that it gets easier for the user to navigate. It is fine to use keyword in the links but make sure that you link it only to a relevant page on your website. This can help you improve the rank of other webpages in your website.
Always use relevant, high quality links that go out of your website. This builds a trust to Google that what you are referring to is important and useful. And this might eventually push your website to higher position in the search results. And, keep away from bad and low quality links. Then again, there are few tiny basic mistakes that newbies tend to do.
Things that one should NOT do for SEO
#1 Stuffing content with keywords.
This was an old trick and is lethal, if you do it now. See that they keyword density is in between 10-15%of your content and not more than it. And also, include they keyword only if it naturally goes with the sentence. Do not stuff them everywhere you like because that will only pull you down and down and down.
#2 Stealing content.
This is the worst possible thing one can do. We write to share our views to our readers and not do a Ctrl+C and Ctrl+V. Although most don’t do this, some get misguided into the trap.
#3 Building unnatural links.
You must’ve heard that the more the number of links, the better it is. And someone might have even suggested you to get links from automated bots. No! Do not blindly build links bearing an impression that it will get your page higher in the list. The opposite, exactly, will happen.
#4 Writing large amounts of useless content.
Although content is the king, it doesn’t mean that you write more and more useless, irrelevant content just to increase the number of blog posts. Remember, the lower the quality of content, the lower will be the rank of the page. Write content that is useful and relevant to the topic.
Stealing content also includes the “rewriting articles” and Google is smart in identifying the stuff even if copyscape.com misses it ! Know about the Google panda which takes care of spam and useless content. Useful I mean = New and Unique content.
These are few important tips to follow and to not follow in 2014, to make the best of your SEO. Hope these will help you with your website.
Here are few more SEO Tips that I covered in 2013 which are still valid and can help you. Although it is dated back 2013, there are useful things that have not changed. Give it a look.























